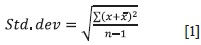
Customers' Attitudes and Perceived Constraints to E-Banking Services: A Survey Study in Albania
Actitudes de los clientes y limitaciones percibidas en relación con los servicios de banca electrónica: una encuesta en Albania
Armelina Lila*
Christian Tanushev**
*Department of Finance, Banking and Accounting, Mediterranean University of Albania, Albania, armelinalila54@gmail.com © https://orcid.org/0009-0003-7124-6438
**Department of Marketing and Strategic Planning, University of National and World Economy, Bulgaria, christiantanush32@outlook.com © https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1172-0519
How to Cite: Lila, A., & Tanushev, C. (2024). Customers' Attitudes and Perceived Constraints to E-Banking Services: A Survey Study in Albania. Apuntes del Cenes, 43 (78). Págs. 99-123. https://doi.org/10.19053/uptc.01203053.v43.n78.2024.17216
Reception date: February 12th, 2024 Approval date: May 13th, 2024
Abstract:
The relevance of the study is determined by the need to identify the level of satisfaction of customers of banks in Albania and the perceived limitations that hinder the development of electronic services. The purpose of the work is the analysis of clients' perception of electronic banking services, the problems of ensuring client satisfaction and the development of proposals for its improvement. The methodological approach hinges on several key components: studying statistical data concerning banking services, conducting two-way analyses to explore variable interactions, conducting surveys to gather user insights, utilizing graphical methods to visualize the results, and employing generalization techniques to summarize research outcomes. The analysis of the development of the banking system of Albania, which showed a significant expansion of electronic services for customers, a substantial increase in the share of electronic transfers in their total number during 2010-2022. A survey of bank customers showed that the availability and flexibility of e-banking services are the most important attributes of their quality; however, there is an impact of perceived limitations on the increase in the number of e-banking users and the need to improve customer service has been proven. Despite the ease and speed of transactions, lower costs and time savings, customers do not rate e-banking as a high-quality service and demonstrate insufficient knowledge about these services. There is a need to improve communication with clients and to reduce costs or provide basic electronic banking services for free. The results and conclusions have practical significance in the development of financial and credit policy by the Government of Albania in the projection of the use of electronic technologies, for bank managers in the planning and marketing of banking services.
Keywords: Internet services, banking institutions, information and communication technologies, user behaviour, satisfaction with product quality, Albania.
JEL Classification: G21, L86, O33.
Resumen:
La relevancia del estudio viene determinada por la necesidad de identificar el nivel de satisfacción de los clientes de los bancos en Albania y las limitaciones percibidas que dificultan el desarrollo de los servicios electrónicos. El objetivo del trabajo es el análisis de la percepción que tienen los clientes de los servicios de banca electrónica, los problemas para garantizar la satisfacción de los clientes y la elaboración de propuestas para su mejora. El enfoque metodológico gira en torno a varios componentes clave: el escrutinio de datos estadísticos relativos a los servicios bancarios, la realización de análisis bidireccionales para explorar las interacciones entre variables, la administración de encuestas para recabar la percepción de los usuarios, la utilización de métodos gráficos para visualizar los resultados y el empleo de técnicas de generalización para resumir los resultados de la investigación. El análisis del desarrollo del sistema bancario de Albania, que mostró una expansión significativa de los servicios electrónicos para los clientes, un aumento significativo de la parte de las transferencias electrónicas en su número total durante 2010-2022. Una encuesta entre los clientes de los bancos mostró que la disponibilidad y la flexibilidad de los servicios de banca electrónica son los atributos más importantes de su calidad; sin embargo, hay un impacto de las limitaciones percibidas en el aumento del número de usuarios de banca electrónica y se ha demostrado la necesidad de mejorar el servicio al cliente. A pesar de la facilidad y rapidez de las transacciones, la reducción de costes y el ahorro de tiempo, los clientes no califican la banca electrónica como un servicio de alta calidad y demuestran un conocimiento insuficiente de estos servicios. Se corrobora la necesidad de mejorar la comunicación con los clientes y reducir el coste o realizar transacciones bancarias electrónicas básicas de forma gratuita. Los resultados y conclusiones tienen importancia práctica para el desarrollo de la política financiera y crediticia del Gobierno de Albania en la proyección del uso de las tecnologías electrónicas, para los gestores bancarios en la planificación y comercialización de los servicios bancarios.
Palabras clave: servicios de Internet, entidades bancarias, tecnologías de la información y la comunicación, comportamiento de los usuarios, satisfacción con la calidad del producto, Albania.
INTRODUCTION
The transformation of the world economy in the conditions of the rapid development of digital technologies and communications allows the creation of new products and services that are more convenient and profitable for consumers. In the banking sector, specially in Albania, such transformations consist in the transfer of services familiar to customers to an electronic format, which demonstrates its advantages in saving financial resources, reducing the time for customer service, the availability of transactions at any time convenient for the customer, and more individualized service. However, the effectiveness of the use of electronic banking services will be greater if customer satisfaction and involvement in the use of these services increases. In connection with the recent increase in the relevance of studying the behaviour of bank customers, there is a need to investigate the satisfaction of customers with banking services and their attitude to electronic banking, as well as to identify the foreseeable limitations that inhibit the spread of the use of electronic banking services.
Issues related to the development of banking activity in the period of digitization were studied by Albanian, Dutch, and other scientists. Ismaili and Braimllari (2021) conducted a study on the frequency of electronic banking service usage among Albanian bank account holders. The results revealed that asynchronous transfer modes (ATM) were the most utilized, followed by electronic point of sale (E-POS) and mobile banking, with individuals over 30 years old using electronic banking less frequently than older demographics.
A comprehensive approach to theoretical and empirical studies of bank profitability was considered by Puci et al. (2023). The authors examined the impact of macroeconomic indicators on bank profitability, in particular the impact of gross domestic product growth, inflation, and the real interest rate during 2011-2020. The reasons for the use of Internet banking services by the population of Albania were considered by Habili et al. (2022). In the study, the scientists used primary data obtained during surveys of various bank customers. The collected responses showed that the declein in customers' willingness to use cash is a key element affecting the growth of the use of electronic banking services.
Anamali et al. (2021) found that customer satisfaction depends mainly on trust and efficiency and identify the relationship between the quality of banking services and customer satisfaction with these services. Other factors only indirectly affect customer satisfaction with banking services but are significant. The authors emphasize that after the two financial crises of 1997 and 2008, Albanian clients expect quality service in the service to feel safe, which is offered specifically for their expectations.
Analysis of the use of banking services by surveying bank customers in the Albanian city of Korcha was conducted by Sulillari and Nasto (2020) in order to find out how much people in a particular city know about electronic banking and use it. The authors found insufficient awareness of the population about electronic banking services because the information they possessed was superficial. At the same time, the analysis of the level of use of banking services by the population revealed some limitations related to the following factors: Income level, employment, etc. The researchers found that e-banking services are still relatively new to the banking industry but have been on the rise recently.
Taking into account the increase in the level of informatization of the world economy, the banking sector must constantly improve and expand the range of its services, applying innovative technologies, particularly with the help of innovative behaviour and an individual approach to clients (Markovych, 2024). A study revealing the question of how perceived organizational innovativeness affects the individual level of a manager and whether it is considered an organizational risk, as well as how the gender of respondents helps or hinders the process, was conducted by Kör et al. (2021) on the example of the banking sector in Turkey. The results showed that strategies of self-leadership are positively related to the individual level of the manager. The authors have made a significant contribution by providing suggestions and advice to managers and employees regarding the development of organizational environments that encourage innovation in the technology-oriented sector, specifically banking. The scientists emphasized that thanks to the effective application of innovations, the work process is improved, paperwork is reduced, labour productivity in the industry is increased, costs are reduced, and economic benefits are increased.
Despite previous studies of this issue, the question of the impact on the development of electronic banking services, the attitude of customers to these services and the existing restrictions that prevent the greater spread of electronic services in Albania, requires further and more detailed study. The main goal of the scientific work is the analysis of the banking activity in Albania regarding the introduction of electronic banking and various factors influencing the attitude of bank customers towards the transition to conducting banking transactions with the guarantee of Internet technologies, as well as the development of proposals for improving the perceived usefulness and quality of electronic banking.
The article will investigate the veracity of the following hypotheses:
Therefore, the main questions of this research are signs of perceived usefulness of electronic banking services in Albania and related limitations.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The theoretical foundation of this research is based on the works of Albanian, Dutch, Polish and other scientists from around the globe who have studied the use of electronic banking in various countries. Information on the development of the banking system in Albania, the use of payment instruments by bank clients, and the infrastructure of banks that allows for settlement transactions, was obtained from the official website of the Bank of Albania (2023).
Statistics on the number of commercial banks in Albania for 2010-2022 are taken from the CEIC Data database (CEIC Data, 2022), which collects the most current economic, sectoral, and financial indicators. Internet penetration rate among the population of Albania in 2013, 2020 and 2023 was analysed given data from the web portal DataReportal (Kemp, 2023), which focuses on statistics and development trends, in particular information technologies.
Information on the total number of bank accounts with Internet access in Albania from 2008 to 2020 was obtained from the online platform Statista (Statista Research Department, 2023), which specializes in market and consumer indicators and provides market statistics, consumer, and company information worldwide. The number of online transactions carried out by Albanians in 2022 is taken from the website of the Albanian newspaper Albanian Daily News (Kote, 2023). Information from 240 users of the Internet and owners of banks of big cities in Albania was collected using an online structured survey conducted in 2021. The sample population refers to able-bodied customers who live mainly in the big cities of Albania and are bank owners.
The methodological approach is base don a combination of statistical information analysis, factor analysis, and survey methods, graphic methods, and generalization. This study employs a statistical analysis approach to examine the level of Internet penetration among the population of Albania, the dynamics of the total number of bank accounts with Internet access during the period 2010-2022, the use of payment instruments by their main types for the same period, and the trend of the development of the banking infrastructure of Albania during the period 2015-2022.
A structured survey was employed to gather data from individuals utilizing banking services, which permitted the assessment of the prevalence of electronic banking products and services among Albanian customers. A structured questionnaire was developed, comprising questions on a four-point scale, grouped by each quality dimension and the dependent variable of customer satisfaction. The data were managed and analyzed using Microsoft Excel.
The method of two-way variance analysis permitted tha determination of the interdependence between the availability of information about electronic banking and the level of education of the population, as well as between the reliability and quality of electronic banking services. The application of this method entails the calculation of standard deviation values based on a survey sample of bank customers, according to the following formula (1):
where: x is the value of sample, n is the size of sample.
A graphic method was employed to present data on the growth of the total number of bank accounts with Internet access in Albania are displayed in the form of graphs and charts. Additionally, the data on the shares in the use of banking instruments, particularly by individuals and enterprises, and the development of banking infrastructure (number of facilities and terminals) used for operations in Albania during 2015-2022 were presented.
The application of the generalization method enabled the recording of information obtained during the research process regarding the use of electronic banking in Albania, the attitude of bank customers to the introduction of electronic services and the foreseeable existing restrictions that affect the population's desire to use these services. It also facilitated the formulation of conclusions regarding the factors on which the level of trust in electronic banking depends and the justification of proposals that allow for an increase in the level of trust of clients in electronic banking services. Finally, it determined further approaches to the study of this issue.
RESULTS
Development of the Banking System and Electronic Banking in Albania
In order to maintain its competitiveness in the market of these services, the banking institution must expand the range of its services, adapting to modern trends in the development of technologies in the world. One of the areas successfully used in banking is electronic banking, the essence of which is self-service for clients. Banks should develop electronic banking services with the objective of satisfying customers as much as possible. To achieve this, it is essential to identify the most important attributes of the quality of these services and to consider customer expectations regarding accuracy, security, network speed, and user-friendliness. Primarily, clients' primary demand for electronic banking is the assurance of robust security during operations. This can be regarded as a significant factor in the assessment of the quality of such services (Khodakivska et al., 2022). In addition, when customers decide to use electronic banking, the key element is the ease of use and the ability and skills of a person in information technologies, which increases customer satisfaction (Khlystun, 2023).
Immediately after the transition to a market economy in 1992, the private banking system began to develop in Albania, in which only 2 banks were still operating in 1991: the Bank of Albania and the Agricultural Bank (CEIC Data, 2022). During the transitional period, the number of banks experienced a significant increase, reaching 16 by 2018. As of December 2022, there were 11 institutions that were fully financed by private capital, both foreign and domestic (CEIC Data, 2022).
The majority of products offered by Albanian commercial banks are standard, including deposits, accounts, transfers, and mortgages. Over the course of a lengthy period, deposits constituted the most popular banking service. However, in recent times, the decline in cash transactions has led to a notable increase in the use of other banking products, including loans, debit cards, and overdrafts. The inaugural financial institution to offer electronic products based on information and communication technologies in 2002 was the American Bank of Albania. For a considerable period, numerous other financial institutions attempted to provide electronic services. For instance, Raiffeisen Bank, through its MultiCash offering, provided electronic transfer services exclusively to a select customer base. Following the year 2007, banks began to offer a wide range of electronic banking services. In 2007, Credins Bank initiated this process, followed by Tirana Bank in 2008, BKT in 2009, and Raiffeisen Bank in 2009 (Bank of Albania, 2023). The increase in the number of Internet providers and the competition among them contributes to the reduction in the prices of digital services (Prymostka & Kysil, 2023; Abdullayev et al., 2024). As in other countries, the implementation of e-government, voting, connecting schools to the Internet and the use of information technologies in public services (e-procurement) are being initiated in Albania. The proportion of the population with access to the Internet is rising at a steady pace. In 2013, 51.8% of the population had Internet access, while by 2020, this figure had risen to 69%. At the beginning of 2023, the proportion of the population with Internet access had reached 80.1% (Kemp, 2023). Nevertheless, Albania continues to be included in the group of countries with low rates of Internet penetration.
The number of bank accounts connected to the Internet has a constant upward trend (Figure 1).
As illustrated in Figure 1, the number of bank accounts with Internet access exhibited an average annual growth rate of 10-30% during the analyzed period. This suggests the rapid integration of Internet technologies into the Albanian banking sector. Popular electronic services provided by Albanian commercial banks include ATMs, Internet banking and electronic cards, which are offered by all banks operating in Albania (Table 1).
As it can be seen from Table 1, certain electronic services (POS-terminals, mobile and SMS banking, telephone banking, POS online payment system virtual) are provided by only a few banks. It should be noted that in 2021, compared to the previous year, the number of ATMs increased by 11.4%, and the number of POS terminals increased by 13.12%.
Use of Payment Instruments by Banks in Albania
The progress achieved by the electronic finance sector can be analysed by the state of the use of payment instruments (Figure 2).
Figure 2 illustrates a clear trend in the use of payment instruments. It demonstrates that the use of electronic credit transfers is consistently on the rise, while the use of paper transfers is on the decline. The use of payment instruments varies depending on the user, wether an individual or a business entity (Figure 3).
Figure 3 shows that in 2022 paper credit transfers were made by approximately 58% of individuals and 42% of businesses, and electronic credit transfers by approximately 43% of individuals, while card payments are used by more than 90% of individuals, whereas electronic cash payments were utilized by only natural persons. The use of electronic money for payments commenced in 2015. From 2015 to 2022, the volume of electronic money payments increased fourfold, from 156,300 to 681,700 transactions.
As reported by the Bank of Albania (2022), the volume of mobile banking payments increased by 29%, while the value of these transactions increased by 22%. The expansion of infrastructure and the dissemination of internet access through the proliferation of smartphone ownership represent the primary driving forces behind the surge in the utilization of mobile banking. As indicated by experts, electronic credit transfers have emerged as the most cost-effective tool in the Albanian economy (Kote, 2023).
The infrastructure utilized by banks for the execution of settlement operations has exhibited a notable expansion (Figure 4).
As can be seen from Figure 4, the number of POS terminals and electronic money terminals has the greatest growth tendency, which during 2015-2022 increased by 2.4 times and 5.9 times, respectively. It should be noted that encouraging the use of electronic money tools has an impact on the financial integration of the population by providing access to banking services to low- and middle-income clients (Mishchenko et al., 2022). Despite the positive trend of increasing the number of POS terminals, the majority of them are concentrated in the city of Tirana (83%) (Kote, 2023). The number of ATMs remained almost unchanged during the analysed period and amounted to 855 units in 2022. In the Albanian market, automated teller machines (ATMs) are primarily utilized for cash withdrawals, rather than for payments.
Compared to other countries of the European region in which Albania is located, this nation has a rather low ratio of cardholders to the total population of both debit and credit cards. Even though the Internet as a business environment has brought practical benefits, it is worth noting certain problems associated with it, for example, information overload, danger to privacy and personal information, etc. For instance, approximately 12% of respondents perceive the electronic banking services offered by Albanian banks to be risky (Kote, 2023).
In addition, the introduction of technological innovations in most cases is not only difficult, but also expensive. Nevertheless, there is a discrepancy between the extent to which electronic banking is utilized and the potential for cost savings and market competitiveness that it offers to banks (Palamarchuk & Korkach, 2023). Statistical data on the economic profitability of electronic banking in Albania is absent, but it is obvious that the cost of one transaction carried out using an electronic channel is much lower compared to a non-electronic form of interaction with the customer.
Survey on Customers' Use of Electronic Banking
The interest in the use of electronic banking services by the population may differ depending on some demographic factors, including age, gender, level of education, average income, and so forth.
Additionally, psychographic factors, such as attitudes toward the digitalization of the economy, preferences, and other psychological characteristics, may also influence the use of electronic banking services.
To analyse the attitude of the population of Albania to electronic banking services and their use, a survey was conducted among people of different socio-economic status, which also made it possible to evaluate electronic services from the point of view of professionalism and reliability (Table 2). In the surveyed group, the mean age of the populace stands at 48 years. Within this demographic, 5% hold higher education degrees, while men make up 46% of the respondents. The social status of the respondents is different, as 40% are single, 38% are married, and 22% have another status.
As illustrated in Table 2, over 60% of respondents whose primary source of income is a salary report income from business, entrepreneurial activity, and wages. Additionally, 23% of respondents report income from another source, including assistance from relatives or social assistance. At the same time, the type of income is a factor that can affect the usage of products of electronic banking.
According to the data presented in Table 2, the National Commercial Bank of Albania is preferred by 60% of customers, followed by Raiffeisen Bank and Credins Bank with 31% and 29%, respectively. Other banks are preferred by less than 10% of customers.
Also, during the study, it was found that there is an inequality between urban and rural areas of Albania regarding the use of the Internet, and the distribution of Internet users in cities is higher than in rural areas.
The responses of the respondents to the survey, as presented in Table 2, indicate that the majority of individuals (40%) obtained information about electronic banking from a bank institution, while 56% accessed this information via the Internet. Additionally, 77% of respondents indicated that they received this information from relatives, while 19% reported obtaining it from various sources. The research indicates that the primary source of information is not banking institutions, but the Internet and social networks. These channels should be regarded as genuine marketing avenues for the sale of electronic banking products.
Two-Way Analysis of the Relationship Between Influencing Factors on Customer Perception of Electronic Banking
To establish the correspondence between the factors affecting the attitude of customers to electronic banking services, it is advisable to investigate the relationship between awareness of electronic banking and the level of education of the population (Table 3).
The results of the survey presented in Table 3 indicate that higher education has a favorable effect on the use of electronic banking. Specifically, 89.2% of respondents have some knowledge in this area, and the level of education has a positive effect on the availability of information. A total of 55.4% of individuals who possess knowledge about electronic banking have attained a higher education. The findings of the conducted research provide empirical support for the hypothesis that an individual's level of education exerts an influence on the availability of information and awareness of the possibilities of using electronic banking services.
To conduct an analysis of the comparison of respondents' answers about the reliability and quality of electronic banking services, the data should be displayed in the form of Table 4.
Table 4 shows that about 65% of customers consider the e-banking service as reliable, 13% of respondents consider this service as risky, and 5.8% as unreliable. According to the results of the survey, about 16% of respondents do not have information about either the reliability or the quality of services.
The conducted analysis shows that representatives of the banking sector should work on improving people's perception of the quality and reliability of electronic banking services, since the level of respondents who would like to use these services, according to the data in Table 4, is 92%, and those who use them is 70%. This suggests the existence of perceived constraints on the provision of electronic banking services, which require greater attention from banking sector employees to facilitate future enhancements. Therefore, the research confirms the hypothesis that the perceived usefulness of electronic banking services is related to the extent to which the potential user assesses their quality level. An important role is also played by the availability and flexibility of information channels.
To enhance the future development of electronic banking services, a number of potential strategies may be considered. These include the expansion of the range of electronic banking opportunities and the introduction of price incentives. This implies that the client, having the opportunity to perform all necessary operations with the assistance of electronic banking, will gain a greater advantage than a prolonged stay in a queue at a bank branch. Furthermore, online transactions should be entirely free or significantly less expensive than transactions conducted at physical branches and banks.
However, it should be noted that clients in the financial sector are not ready to use only online channels for communication. Personal contact is beneficial and important, so banks should keep this in mind when promoting services. Therefore, it is impossible to predict which channels of communication with customers will be exactly successful, and it is also impossible to use only one channel, particularly the Internet.
In the context of the accelerated development of digital technologies, it is imperative that bank representatives utilize innovative products that are actively promoted, as this increases the likelihood of their successful dissemination. The advent of electronic banking is contingent upon the existence of a sufficient level of Internet penetration within a given country, as well as the capacity of banks to provide a comprehensive array of services. This will result in the satisfaction of users of the service, who will then act as promoters of the service. Nevertheless, it is also essential to maintain personal communication with the client.
The analysis of the development of the banking system of Albania showed that during the years 2010-2022 the number of electronic services increased, the infrastructure for their provision was expanded, and a gradual transition of customers to the use of payment instruments using the Internet technologies and electronic money was observed. The conducted survey of Albanians of different ages, gender, education, and income levels regarding their attitude and trust in electronic banking services allowed determining the relationship between the socio-demographic features of the client and the possession of information about the electronic services of banks in Albania. A study that was also conducted made it possible to conclude that people who might want to use electronic banking services do not have enough information about their reliability and quality, which indicates the presence of perceived limitations for using electronic banking.
DISCUSSION
The introduction of digital technologies has facilitated the expansion of electronic banking services in Albania. This has resulted in a number of advantages for customers, including enhanced convenience in conducting banking transactions, while banks have also benefited from reduced costs associated with the provision of banking services to customers. Despite the advantages of electronic banking, clients of banks in Albania use these services to a relatively limited extent. This indicates a need for banking institutions to develop measures that will help to increase clients' trust in electronic banking services.
The work examines various factors that can influence the willingness of Albanian bank customers to use electronic services and emphasizes that satisfaction with these services depends on their quality, specially safety and availability.
In a different order of ideas, the study of the impact of the quality of electronic banking services on customer satisfaction and loyalty in the Ethiopian banking industry was carried out by Ayinaddis et al. (2023). The scientists conducted a survey using a questionnaire among 385 participants. The results indicated a significant impact of variables such as responsiveness, reliability, security, and privacy. Moreover, customer satisfaction with the quality of electronic banking services affects their loyalty. In agreement with the aforementioned viewpoint, it is of significant importance to note that banks must direct their efforts towards the enhancement of the speed of response, reliability, and availability of their systems, with the objective of maximizing customer satisfaction and loyalty. Likewise, a study of customer attitudes towards Internet banking in the city of Pokhara, which is the tourist capital of Nepal, was conducted by Shrestha et al. (2020) on the basis of data collected through a customer survey. The findings of the authors' research facilitated improvements in communication between banks and their clients, while simultaneously reducing the costs associated with the expansion of their product portfolios.
According to the results of the analysis, it was emphasized that the factors that influence the desire of consumers to use electronic banking services are the awareness of the usefulness of electronic banking, saving time for making payments and lower costs for bank commissions compared to the cost of transactions carried out through bank cashier.
A comparable perspective is espoused by Ismael et al. (2021). The authors examined the factors influencing consumers' intention to use not only Internet banking but also other digital financial services in Egypt. Their findings demonstrated that perceived usefulness and trust by customers significantly and positively influence consumers' intention to use digital financial services. At the same time, Vovchenko (2021) and Niyazbekova et al. (2023) emphasized that ease of use, perception of risks and cost do not affect consumer intentions. In addition, Aboobucker (2020) conducted a survey of 186 bank customers, which demonstrated that the perceived usefulness and convenience of using electronic banking influence customers' intention to use it. However, perceived ease of use and awareness did not show a significant relationship, and age and gender did not cause a significant moderating effect.
We must totally agree with the scientist Le-Hoang (2021) that among the most important factors that contribute to the use of electronic banking by clients, the following can be highlighted: ease of use, usefulness, trust, expected efficiency, social influence, promotion. However, the scientist identifies expected efficiency as the least influential factor. Specifically, confirming these factors, Karim et al. (2020) determine that perceived security has a stronger influence on trust and perceived ease of use. Instead, Majumdar and Pujari (2021) rightly note that the perception of usefulness and availability of information are among the main factors that influence the adoption and level of use of mobile banking programs in the United Arab Emirates.
In examining the factors that influence consumer behavior regarding electronic banking services, it is essential to consider the impact of changes in the network of bank branches, including the opening of new branches or the closing of existing ones. Thus, Zhou et al. (2020) showed that the opening of branches increases the number of customer transactions, but the opening of the first branch may lead to a decrease in the use of online banking in the short term, and vice versa, the closing of branches promotes the migration of customers from the branch channel bank to online banking.
Agreeing with the scientists' point of view, it should be noted the existence of interdependence between the change in the number of working bank branches and the decrease or increase in the use of electronic banking by clients. Similar research on the example of retail trade was conducted by Kumar et al. (2019), whose found that the opening of sales points led to an increase in online purchases by store customers, explaining this consumer behaviour by the fact that customers make more online purchases due to increased interaction with the store, while thereby experiencing a reduction in the risk of online shopping due to the possibility of returning the product to the store. Considering the aforementioned conclusions, it is evident that the banking sector can benefit from a similar approach. In this case, the distribution channel is the bank branch, which can be utilized to stimulate the use of banking services. Clients' awareness of the risks or safety of making payments by electronic means undoubtedly influences their use of such means. A study of the influence of perceived ease of use and perceived risk on the intention to make payments through a mobile phone among the population of Pakistan was conducted by Islam et al. (2020). The study emphasized that the perception of risk is considered a significant negative factor for establishing trust from consumers.
A significant impact on the expansion of the use of electronic services was caused by the introduction of restrictions due to the spread of the COVID-19 pandemic. A study in this direction was conducted by Hoxhaj and Muharremi (2022), who evaluated the influence of the following factors on the use of online banking during the pandemic: age, gender, education, income level, perception of security, usefulness, and ease of use. The researchers emphasized that the convenience, speed, and ease of use of online services did not affect the use of online banking during the pandemic.
In addition, the actual and potential impact of the pandemic on the financial markets has been studied by Wójcik and Ioannou (2020), who aptly note that the use of new financial technologies is likely to accelerate, affecting retail banking in particular. The paper emphasizes the advantages of using electronic banking in comparison with performing payment operations at the cash desk of a bank branch and highlights the economic benefits of this method of performing operations. Likewise, Jolly (2016) notes that clients can use electronic banking to carry out almost all banking operations, requiring only an Internet connection. Among the advantages of electronic banking, the researcher mentions: simplicity, 24-hour access to operations, and economic efficiency. The study on the influence of the quality of electronic services in retail online banking on customer satisfaction during the restrictions of the COVID-19 pandemic was carried out by Mwiya et al. (2022) and found that security, privacy, speed of response, efficiency, execution, and reliability are definitely related to the quality of electronic services and affect customer satisfaction. Emphasizing the need to improve the quality of electronic services, it should be noted that improving these indicators in the Albanian banking sector will contribute to increasing customer satisfaction and the use of online banking.
Furthermore, the direct impact of the quality of electronic banking services on the satisfaction and loyalty of customers of the Commercial Bank of Ethiopia in Bahir Dar was investigated by Beshir and Zelalem (2020). The authors identified seven dimensions of service quality: efficiency, reliability, speed of response, ease, product portfolio, privacy, and cost. The findings of the study conducted by the scientist indicated a significant impact of efficiency, responsiveness, ease, privacy, and commission on satisfaction, as well as a significant effect of satisfaction on loyalty.
Consequently, an analysis of the findings of previous research conducted by other scientists on the impact of various factors on the formation of bank customers' satisfaction, trust, and intention to utilize electronic banking services in the future reveals a genuine concern regarding this issue. The majority of scientific research was conducted based on the results of customer surveys. The results of the aforementioned research indicate a correlation between customers' perceptions of the reliability and quality of electronic banking and their willingness to utilize these services. This finding is corroborated by the perspectives of other scientists who advocate for enhanced communication between banks and customers to facilitate the growth of electronic banking.
CONCLUSIONS
The research shows that in modern conditions of the development of information and telecommunications technologies, banking tools for carrying out operations tend to be transformed into electronic format, making them more convenient for clients and economically more profitable for the banking sector.
The goal set in this work and the analysis of the main problems of the attitude of Albanian bank customers to electronic services allowed us to formulate the following conclusions. The analysis of the development of the banking system of Albania during 2010-2022 was characterized by a significant increase in the number of bank accounts with access to the Internet, the rapid dynamics of the expansion of the banking infrastructure, which provides the opportunity to use electronic banking services. It was established that the number of POS terminals, 83% of which are concentrated in Tirana, the capital of Albania, had the greatest growth dynamics. It was found that starting from 2018, the part of credit transfers in paper form decreased and the total volume of such transfers increased in electronic form. By conducting a survey among the population with different demographic characteristics, it was found that for more than 60% of respondents, the main source of income is the salary of an employee, and Raiffeisen Bank (31%) and Credins Bank (29%) are the most chosen banks.
The results of the study on the relationship between customers of banks in Albania and their use of electronic banking information, in conjunction with the level of education of the population, have confirmed the hypothesis that respondents with higher education levels possess greater knowledge of banking services and are more frequently aware of the benefits of electronic banking. It is evident that a significant proportion of customers (60.3%) consider electronic banking services to be reliable, while 13% perceive them as risky and 5.8% as unreliable. It is argued that the number of bank clients who would like to use electronic banking services is greater (92%) than those who already use them (70%). This indicates the presence of perceived limitations and the need to improve the work of bank employees with clients in the direction of clarification for them the benefits of using electronic banking.
The hypothesis that the expected usefulness of electronic banking services is related to the degree of the client's assessment of their quality level was confirmed through the analysis of the dependence between reliability and quality of electronic banking services. It is justified that in order to improve the attitude of customers towards the use of electronic banking, it is imperative to enhance the security, confidentiality, and availability of these services, which will increase the trust of customers and stimulate the desire to use them. To improve electronic banking services, it is proposed to expand the range of possibilities of these services and to develop price lists of incentives that provide for the transfer of online transactions to a free basis or a reduction in their cost compared to transactions in branches and banks.
The proposal has practical significance and can be applied by the Government of Albania in the development of financial and credit policy and decision-making on the use of electronic technologies in the banking sector. Furthermore, it can be utilized by bank managers and employees in the development of strategies for communicating with clients, explaining to them the benefits of using electronic services and for marketing planning in the banking sector in Albania.
The primary focus of future research will be on the identification of the factors that contribute to the imposition of restrictions on customers' use of electronic banking services.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
The authors would like to express their gratitude to the editorial team of Apuntes del Cenes and the reviewers for their invaluable feedback and constructive suggestions, which significantly enhanced the quality of this paper.
DECLARATION OF CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors of this article declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
AUTHOR'S CONTRIBUTION
Armelina Lila was instrumental in conceptualizing the research, curating and analyzing data, conducting investigations, developing methodology, administering the project, managing resources, supervising the process, validating results, visualizing data, and drafting the original manuscript.
Christian Tanushev was involved in conceptualization, literature review, methodological development, data collection, fieldwork, and contributed to both drafting and editing the manuscript.
FUNDING
This research received no external funding.
REFERENCES
[1] Abdullayev, K., Abdullayev, R., Yusifov, E., Babazade, I., & Fataliyeva, G. (2024). Main Areas of Development of the Digital Economy in the Republic of Azerbaijan. Economics of Development, 23(1), 78-88. https://doi.org/10.57111/econ/1.2024.78
[2] Aboobucker, I. 2020. What Motivates the Adoption Intention of E-Banking Services: The Moderating Role of Age and Gender. Asian Journal of Management Studies, 1(2), 128-143. https://doi.org/10.4038/ajms.v1i2.38
[3] Kote, K. (2023, 10 de marzo). Albanians Performed over Five Mln Banking Actions Online in 2022. Albanian Daily News. https://albaniandailynews.com/news/albanians-performed-over-five-mln-banking-actions-online-in-2022-
[4] Anamali, A., Zisi, A., & Shosha, B. (2021). Banking Service in Albania: Satisfied… from What? Universal Journal of Accounting and Finance, 9(4), 735-744. https://doi.org/10.13189/ujaf.2021.090419
[5] Ayinaddis, S. G., Taye, B. A., & Yirsaw, B. G. (2023). Examining the Effect of Electronic Banking Service Quality on Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty: An Implication for Technological Innovation. Journal of Innovation and Entrepreneurship, 12,22. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13731-023-00287-y
[6] Bank of Albania. (2022). Annual Report 2021. https://www.bankofalbania.org/Publications/Periodic/Annual_Report/Annual_Report_2021.html
[7] Bank of Albania. (2023). Payment Systems Statistics of Albania. https://www.bankofalbania.org/Payments/Payment_systems_statistics/
[8] Beshir, E. S., & Zelalem, B. A. (2020). The Effect of E-Banking Service Quality on Customer's Satisfaction and Loyalty. The Strategic Journal of Business & Change Management, 7(3), 818-832. https://doi.org/10.61426/sjbcm.v7i3.1694
[9] CEIC Data (2022). Albania Number of Commercial Banks. CEIC. https://www.ceicdata.com/en/albania/banks-concentration-indicators/no-of-commercial-banks
[10] Habili, M., Muharremi, O., & Hoxhaj, M. (2022). Analysis of the Variables Influencing People's Propensity to Use Online Banking Services in Albania. International Journal of Finance & Banking Studies, 11(4), 58-65.https://doi.org/10.20525/ijfbs.v11i4.2266
[11] Hoxhaj, M., & Muharremi, O. (2022). Coronavirus: An Empirical Study of the Pandemic's Effect on Albanian Online Banking Services. International Journal of Electronic Banking, 3(2), 121-143. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJEBANK.2022.122229
[12] Islam, T., Saif-Ur-Rehman, Abid, Ch. M. S., & Ahmer, Z. (2020). How Perceptions about Ease of Use and Risk Explain Intention to Use Mobile Payment Services in Pakistan? The Mediating Role of Perceived Trust. Pakistan Journal of Commerce and Social Sciences, 14(1), 34-48.
[13] Ismael, D. M., Salah Ali, S., Adel Elsharkawi, S. (2021). Consumers' Intention to Adopt Digital Financial Services in Egypt: An Extended Technology Acceptance Model. Journal of Alexandria University for Administrative Sciences, 58(5), 273-311. https://doi.org/10.21608/acj.2021.208142
[14] Ismaili, E., & Braimllari, A. (2021). Factors Influencing the Frequency of Use of E-Banking Services in Albania. In 4th International Conference on Recent Trends and Applications in Computer Science and Information Technology. CEUR Workshop Proceedings. https://ceur-ws.org/Vol-2872/paper08.pdf
[15] Jolly, V. (2016). The Influence of Internet Banking on the Efficiency and Cost Savings for Banks' Customers. International Journal of Social Sciences and Management, 3(3), 163-170. https://doi.org/10.3126/ijssm.v3i3.15257
[16] Karim, M.W., Ulfy, M.A., & Huda, N. (2020). Determining Intention to Use Smartphone Banking Application among Millennial Cohort in Malaysia. International Journal of Management and Sustainability, 9(1), 43-53. https://doi.org/10.18488/journal.11.2020.91.43.53
[17] Kemp, S. (2023). Digital 2023: Albania. DataReportal. https://datareportal.com/reports/digital-2023-albania.
[18] Khlystun, D. (2023). Improvement of the System for Management of Organization's Communication with Consumers by Automating the Service Provision Process in the CRM Environment. Economic Bulletin of Cherkasy State Technological University, 23(1), 19-28. https://doi.org/10.24025/2306-4420.68.2023.284535
[19] Khodakivska, O., Kobets, S., Bachkir, I., Martynova, L., Klochan, V., Klochan, I., & Hnatenko, I. (2022). Sustainable Development of Regions: Modeling the Management of Economic Security of Innovative Entrepreneurship. International Journal of Advanced and Applied Sciences, 9(3), 31-38.
[20] Kör, B., Wakkee, I., & Van der Sijde, P. (2021). How to promote Managers' Innovative Behavior at Work: Individual Factors and Perceptions. Technovation, 99, 102127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.technovation.2020.102127
[21] Kumar, A., Mehra, A., & Kumar, S. (2019). Why Do Stores Drive Online Sales? Evidence of Underlying Mechanisms from a Multichannel Retailer. Information Systems Research, 30(1), 319-338. https://doi.org/10.1287/isre.2018.0814
[22] Le-Hoang, P. V. (2021). Intention to Use M-Banking Application: An Empirical Study in Ho Chi Minh City. Independent Journal of Management & Production, 12(2), 637-653. https://doi.org/10.14807/ijmp.v12i2.1256
[23] Majumdar, S., & Pujari, V. (2021). Exploring Usage of Mobile Banking Apps in the UAE: A Categorical Regression Analysis. Journal of Financial Services Marketing, 27, 177-189. https://doi.org/10.1057/s41264-021-00112-1
[24] Markovych, I. (2024). The Influence of Behavioral Encouragement (Monitoring) on the Culture of Consumption. Economic Forum, 1(4), 32-37.
[25] Mishchenko, V., Naumenkova, S., Grytsenko, A., & Mishchenko, S. (2022). Operational Risk Management of Using Electronic and Mobile Money. Banks and Bank Systems, 17(3), 142-157. https://doi.org/10.21511/bbs.17(3).2022.12
[26] Mwiya, B., Katai, M., Bwalya, J., Kayekesi, M., Kaonga, S., Kasanda, E., Munyonzwe, C., Kaulungombe, B., Sakala, E., Muyenga, A., & Mwenya, D. (2022). Examining the Effects of Electronic Service Quality on Online Banking Customer Satisfaction: Evidence from Zambia. Cogent Business & Management, 9(1), 2143017. https://doi.org/10.1080/23311975.2022.2143017
[27] Niyazbekova, S., Zverkova, A., Sokolinskaya, N., & Kerimkhulle, S. (2023). Features of the "Green" Strategies for the Development of Banks. E3S Web of Conferences, 402, 08029. https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/202340208029
[28] Palamarchuk, O., & Korkach, I. (2023). Trends in the Development of Digital Marketing in Modern Business Conditions. University Economic Bulletin, 18(2), 63-68. https://doi.org/10.31470/2306-546X-2023-57-63-68
[29] Prymostka, L., & Kysil, T. (2023). Intelligent Information Systems of the Banking Sector: General Characteristics and Information Environment. Scientific Bulletin of Mukachevo State University. Series "Economics", 10(4), 43-53. https://doi.org/10.52566/msu-econ4.2023.43
[30] Puci, J., Draci, P., Demi, A. & Merja, Z. (2023). An Assessment of Bank Profitability: Evidence from Albania. International Journal of Applied Economics, Finance and Accounting, 16(1), 86-96. https://doi.org/10.33094/ijaefa.v16i1.924
[31] Shrestha, D., Wenan, T., Rajkarnikar, N., & Jeong, S. R. (2020). Consumers Attitude Towards Internet Banking Services in an Underdeveloped Country: A Case of Pokhara, Nepal. Journal of Internet Computing and Services, 21(5), 75-85.
[32] Statista Research Department (2023, 4 sep.). Total Number of Internet Accessible Bank Accounts in Albania from 2008 to 2020. 2021. Statista. https://www.statista.com/statistics/875033/number-of-internet-bank-accounts-albania/
[33] Sulillari, J., & Nasto, K. (2020). E-Banking Services Knowledge and Usage, the Case of Korca city, Albania. International Journal of New Economics and Social Sciences, 12(2), 9-22.
[34] Vovchenko, O. (2021). Development of the Banks' Risk Management System under Conditions of Uncertainty. Economics of Development, 20(4), 8-15. https://doi.org/10.57111/econ.20(4).2021.8-15
[35] Wójcik, D., & Ioannou, S. (2020). COVID-19 and Finance: Market Developments so far and Potential Impacts on the Financial Sector and Centers. Tijdschrift Voor Economische en Sociale Geografie, 111(3), 387-400. https://doi.org/10.1111/tesg.12434
[36] Zhou, M., Geng, D., Abhishek, V., & Li, B. (2020). When the Bank Comes to You: Branch Network and Customer Omnichannel Banking Behavior. Information Systems Research, 31(1), 176-197. https://doi.org/10.1287/isre.2019.0880